
ASA/Astrooptik Newton Focal reducer 0.73
A Why this reducer ?
This optical master piece has no equivalent in the world !
According to Cyril HOUSSEAU who did the main mirror, the reasonnable choice to keep collimation/focus tolerance/optical quality at an acceptable level is f/d=4.
While correcting coma, this reducer gives in the same time another kick to the telescope speed who will work at f/d=2.9, with a corrected field up to 18mm.
http://www.astrooptik.com/index_korrektor.htm
And i love poetic sentences like this one from philipp KELLER / Astrooptik:
"This reducer, combined with a VERY GOOD parabolic mirror will beat every single Apochromat out there and you will have a much faster focal ratio."
I discovered the astrooptik reducer since a long time, thanks to cristophe demeautis.
As Philipp KELLER concentrates his work on big telescopes, you must now contact ASA for buying this highly recommended little GEM :
http://www.astrosysteme.at/ikreator/asa/cms_pub/content_93-en.html
B Spotdiagram courtesy of philipp KELLER / Astrooptik

I plan to use the reducer with an ICX285 based ccd camera, so i used the spotdiagram to make a quick and dirty work to compare this reducer to my current setup.
Thanks to the scale, i add the pixel pattern to the spot diagram.
If you see the below result, you can notice the big box, is approximatively 4 pixels wide.
One little square mimics one square pixel of 6.45?m ...
This is a dream compared to SC telescopes "8-) used with a focal reducer :
Last thing, as i use LRGB imaging, i get the idea to add the 5 wavelength to see the star shape in the L channel :
It should be OK "8-)
C Vignetting from philipp KELLER / Astrooptik
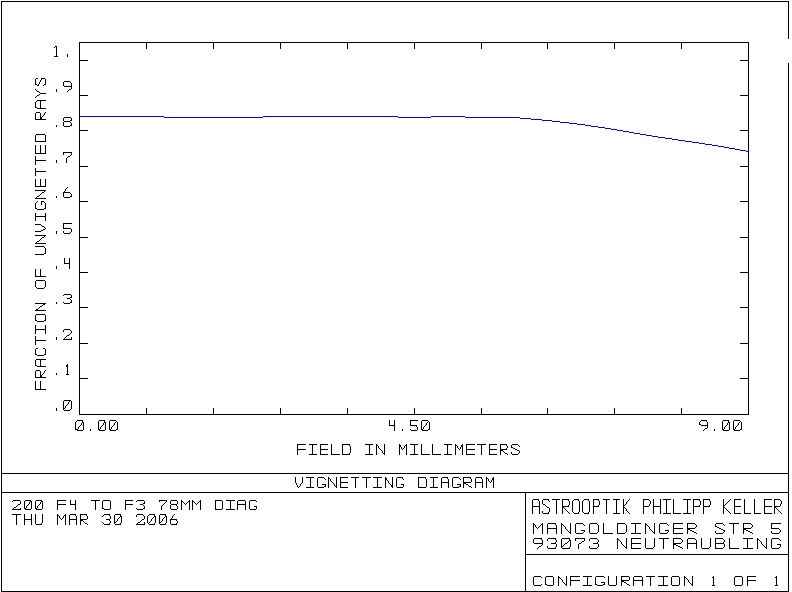
At f/d=4 , the 2" barrel always generate some vignetting, but as i'm convinced that flats is an absolute must for good quality images, a light vignetting is not a problem.
If you don't want any vignetting, with the goal of collecting every photon that falls in the telescope, you muste take a 3 inch focuser and a wynne corrector.
D Layout from philipp KELLER / Astrooptik

D Real life ... on the full corrected field with a KAF3200E sensor
One must be aware that low f/d are very demanding. I found nearly impossible to go below F3.0, so i only use 184mm of the mirror.
This makes a 7" F:D=3.2 instruments, what i loose in light is my gain in tolerances. And i keep a 584mm focal distance telescopes who covers more than one squared degree in the sky.
I measured the focal lenght, and i have f=610mm
Here are the corner and the center from a KAF3200E field in L :

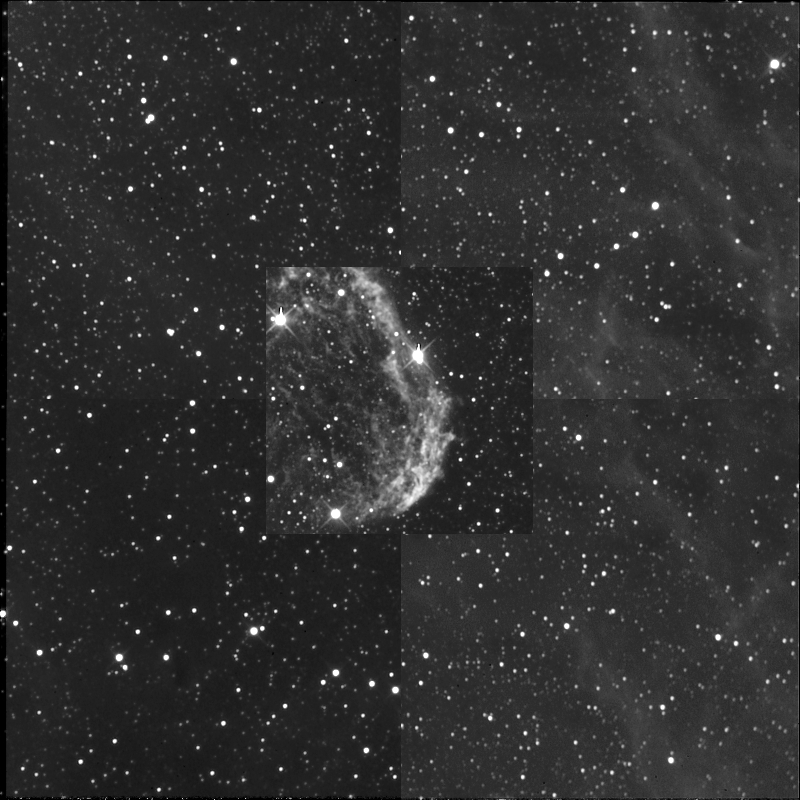
Another test with longer imaging time and astonomik Ha filter :
NGC6888 30 exposures of 180s , one hour imaging :
quite fast "8-)
A FSQ needs two hours , and a FS78 5 hours to achieve the same S/B ratio.

The corner's:

The corresponding CCD inspector report :
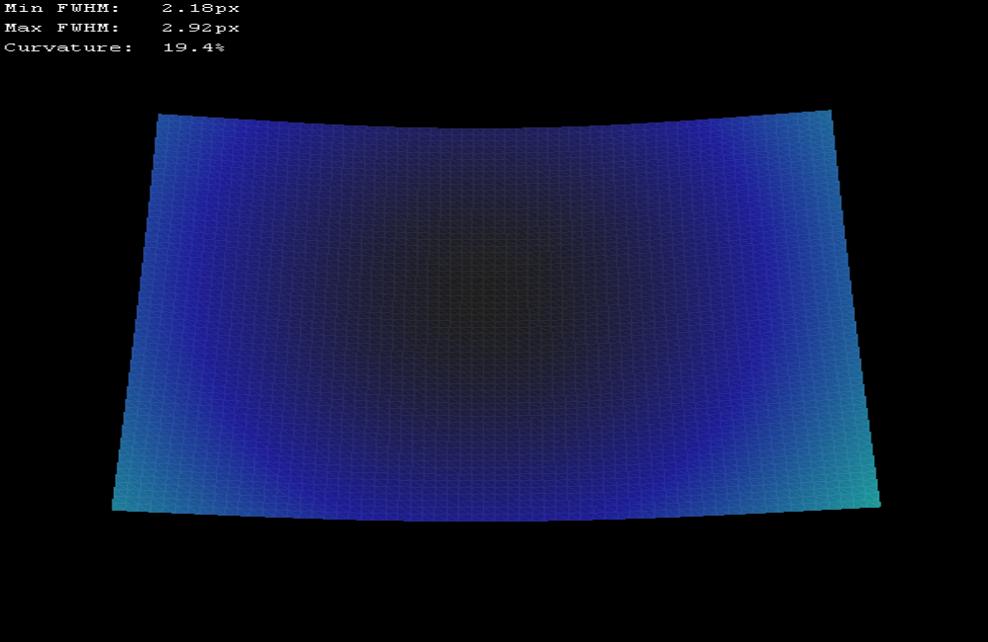
On individual exposure :
The blue part is under 2,2px.
Please note you must really respect the back focus to have good result, and you can't avoid problems due to very low f/d ratio.
Flat image :

A profile line in the diagonal line :
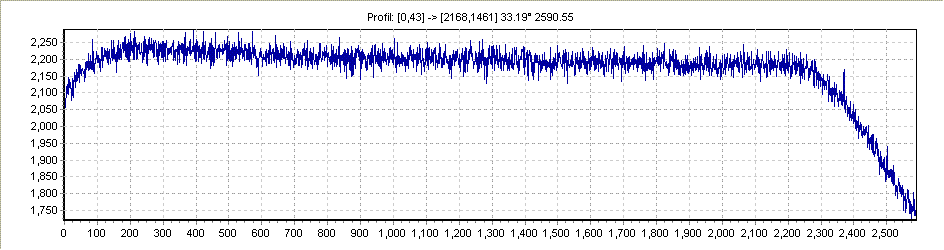
There is a 2200 circle covered with 100% of the light, and the fast decreasing border indicates a vignetting due to the 31.75mm filter.
In this scope , everything is used at 100%
E Use of the reducer with a smaller sensor.
On a smaller CCD sensor, the field is even better, here is the CCD inspector analysis from a ATIK16HR camera :

The field is really flat ...
The focal distance lies aound f=610mm , this makes 2.3arcseconds per pixel. On the 60s L ( astrodon filter ) it gives 3.5" stars.
With the astronomik 13nm Ha filter, this values is even better at 2,3" , nearly 100% of the incoming light hits in one pixel.
F Focusing such a short f/d ... is it possible ???
Focusing curve :

One motor step is a very tiny 10?m !
My selfmade electronic , the starlight motor and focusmax are working extremly well, the focus is the same every time i focus within a couple of minutes, and thanks to carbon tube properties ( extrem stiffness and low thermal expansion ) , the focus remains the same within all the night.